Load compensation
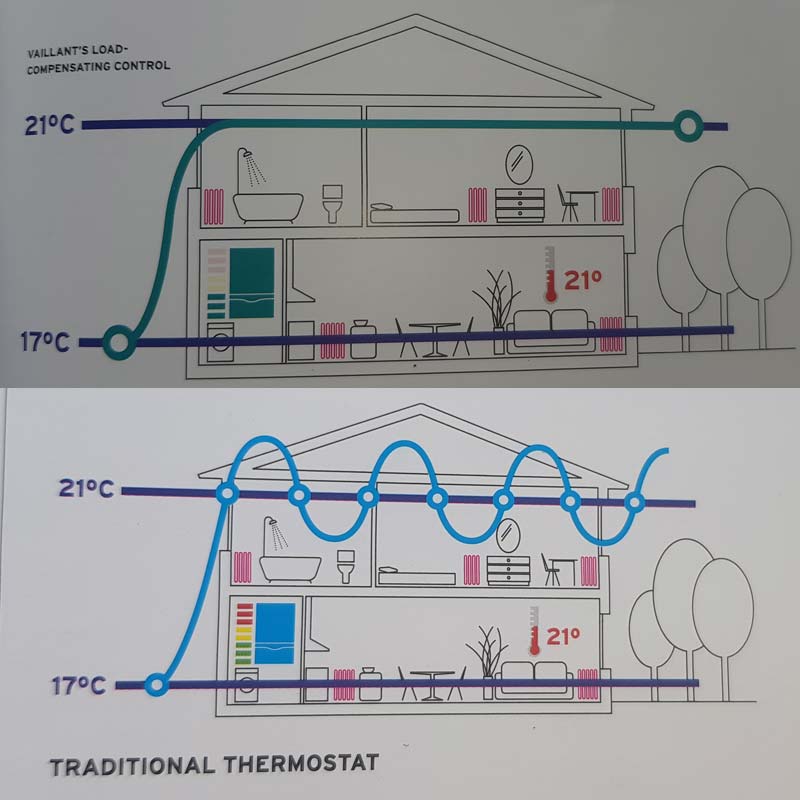
Load compensation relates to the way a heating Control manages the boiler output to reach a target temperature within the signature room (where the thermostat is fitted). This type of control is a "modulating control".
With load compensation, the control is constantly monitoring the room temperature and as the target temperature for the room approaches, the control will tell the boiler to modulate to a lower system temperature so that the target room temperature is not exceeded. Using this form of intelligent control, the boiler is more frequently kept at lower temperature and in full condensing mode, therefore is more efficient. In addition, as the boiler is not operating at its maximum and is not constantly turning on and off, there is less wear and tear on the parts.
Vaillant has one of the most advanced range of Controls that, combined with the eBUS protocol, enables load compensation to ensure maximum comfort in the most efficient and cost effective operation. Load Compensation is also an additional energy efficiency measure to comply with Boiler PluS all Vaillant's modulating controls meet this legal requirement.
Drayton Wireless Digistat and RF Room Thermostat
 RF601_31003.jpg)
 PDF - Drayton Wireless Room-stat RF - Installation instructions
PDF - Drayton Wireless Room-stat RF - Installation instructions
Honeywell ST9400A & ST9400C Programmer Installation

 PDF - Honeywell ST9400A & ST9400C Programmer Installation Instructions
PDF - Honeywell ST9400A & ST9400C Programmer Installation Instructions
Frost Thermostat
mg src="../../images/Text/central_heating/Controls/frost_thermostat.jpg" alt="Frost thermostat" width="167" height="167" hspace="100" />
- Prise - £15
- provides automatic frost protection to boilers and pipework situated in risk areas
- cold weather compensation device
- fix 1.5m from ground level in the hallway
- requires a permanent live connection
- Temp Setting Range: 3°C - 20°C
Pressure Gauges

- Price - £8
- should be capable of reading a pressure range of 0 to 4 bars
- Bottom entry 1/4" BSP male
- Max working temperature 80°C
Thermostatic Radiator Valves

- Temperature Sensor - used to control heat output
- TRV can be installed with a remote sensing element
- TRVs should not be fitted on all radiators in a system (usually not fitted in the room with a room thermostat)
- A Bypass MUST be fitted to prevent the pump burning out
- Retaining Cap - holds the pin down when thermostatic head is taken off
- TRVs have replaceable packing gland
Air Separator

- Price - £11
- allows cold feed and open vent to be joined close together
- reduces noise in the system
- lowers risk of corrosion
- Automatically and progressively eliminates air from the system
- Reduces pump failure
Anti-gravity Valve
- prevent unwanted circulation
- Normally located vertically on the flow above boiler
Pipe Frost Thermostat
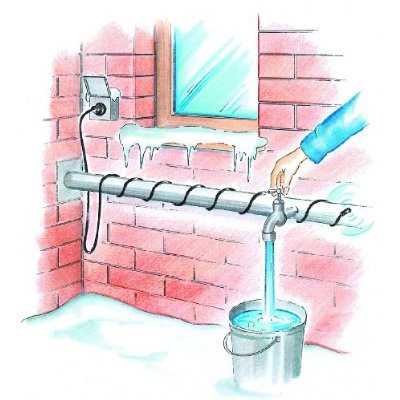
- used in conjunction with a frost stat
- 4 metres long / 60 watt
- Includes a built in automatic thermostat which turns the cable on when temperature falls below 5*C
- Ideal for use on water, oil or fuel pipes, metal or plastic pipes
- The cable should be wound round the pipe or fastened alongside the pipe with cable ties (not included)
Electromechanical Time Switch

- for use with control systems where heating and domestic hot water are required at the same time
- controls either space heating or hot water, or both together
Motorized Zone Valves
- Control water flow from boiler to heating and hot water circuits
- Three-port Motorized Valve:
- works in conjunction with a room and cylinder thermostat
- controls water flow to two destinations, usually space heating and hot water
- Diverting Type :
- selective priority for the domestic hot water
- only one outlet open at a time
- Mid Position Type :
- both outlets open can be open at a time
- Two-port Motorized Zone Valve

- used on gravity domestic hot water and pumped central heating systems
- controls flow to a single destination, either to the hot water cylinder circuit or to the heating circuit
- Lock-shield Valve – to balance the system and overcome tampering
Air Release Valve

- installed on the positive side and highest point of the system
- there is always one inside the boiler
Automatic Bypass Valve

- Installed immediately after the pump
- Protects the pump
- 22mm pipework
- maintains MIN water flow rate through the boiler
- reduces system noise and increases pump life
- particularly used in systems with TRVs
Cylinder Thermostat

- provides temperature control for stored hot water
- connected to the circulating pump or boiler or operates a motorized valve
- strapped around the third of the way up from the bottom of the cylinder
- working principle - bi-metal strip sensor device
Room Thermostat
- can directly switch on a circulating pump or boiler, or to operate a motorized valve
- Positioned in the coolest room to be heated and 2m away from radiator
- 1.5m up from the floor level
- Types of Room Thermostats :
- Bimetal sensor type Room Thermostat
- Vapor Capsule type Room Thermostat
- Vapor Capsule type Room Thermostat (with anticipator)
- Intelligent Room Thermostat

- incorporates an energy delay start feature which increases fuel economy
- relies on an electronic sensor for its operation
- Programmable Room Thermostat

- combines the functions of a time switch and room thermostat
- automatically controls the room temperature at different levels throughout the day
- set target temperatures for different periods of time
Heat Anticipator
- A heat anticipator generates a small amount of additional heat to the sensing element while the heating appliance is operating.
- This opens the heating contacts slightly early to prevent the space temperature from greatly overshooting the thermostat setting.
- A mechanical heat anticipator is generally adjustable and should be set to the current flowing in the heating control circuit when the system is operating.
Boiler Energy Manager

- reduces unnecessary boiler cycling
Programmer/Timer

- used to provide time control for the system
- can be used on gravity, primary and fully pumped systems

 RF601_31003.jpg)
 PDF - Drayton Wireless Room-stat RF - Installation instructions
PDF - Drayton Wireless Room-stat RF - Installation instructions
 PDF - Honeywell ST9400A & ST9400C Programmer Installation Instructions
PDF - Honeywell ST9400A & ST9400C Programmer Installation Instructions